How Does Concentration Affect Cell Potential
Because ΔG 0 at equilibrium the. I carried out some experiments where I varied the concentration of a copper half cell and compared the potential difference against a silver half cell.

Concentration Cells Cell Potential Calculations Electrochemistry Youtube
This is where the temperature dependence comes from.

. I The Nernst Equation Reported cell potentials are typically measured under standard conditions. How does potassium affect the resting membrane potential. It checks out fine with the Nernst Equation but conceptually voltage is the driving force or energy of the current.
As temperature increases so does the voltage for all 3 types of cells. Like how the standard reduction potential isnt based on moles of reactant. Here the effect of temperature and concentration on the voltage of a Daniell cell is quantified.
How do temperature and concentration affect Ecell of a half cell An ongoing discussion beginning back in 2003. As the reaction shifts toward the right Ecathode increases which therefore increases Ecell since Ecell Ecathode - Eanode. Because the concentration in only one side of the cell has changed the concentration gradient across both sides of the cell becomes steeper.
We have the Nerst Equation. Changing the concentration of one solution in the cell will increase the voltage potential of the cell because you are putting the system further out of equilibrium. Factors such as the metals constituting the electrodes play a large role in determining the voltage potential of a galvanic cell however other variables such as concentration and temperature do affect the voltage produced.
The concentration effect in an electrochemical cell is described by The Nernst Equation. A There is this nifty little mathematical relationship called the Nernst equation that allows us to deal with the cell potential of nonstandard solutio. For instance as potassium levels increase in the extracellular space the magnitude of the concentration gradient for potassium across the myocyte diminishes thus decreasing the resting membrane potential that is 90 mV to 80 mV.
Im a bit confused about why in 1c if the air pressure is lower and there is a lower concentration of oxygen why the cell potential decreasesIt checks out fine with the Nernst Equation but conceptually voltage is the driving force or energy of the current. The electrode potential difference between the two half-cells can be calculated using the Nernst equation. Effect of Concentration Changes on Cell Potential 1.
Δ E Δ S n F T Δ H n F. It has been determined that cell potentials are related to concentrations of reactants and products and to. Δ G Δ H T Δ S.
If we alter these conditions in this case. Zns Cu2 aq Zn2 aq Cus E0 cell 11V. View the full answer.
Kc M2 M s cannot appear in the equilibrium law equation as its not in the same state. The Nernst equation allows us to determine the spontaneous direction of any redox reaction under any reaction conditions from values of the relevant standard electrode potentials. This decreases the difference between the inside and outside of the cell.
Why does changing the extracellular K concentration have more of an effect on the membrane potential than changing the extracellular Na concentration. Concentration cells work to establish equilibrium by transferring electrons from the cell with the lower concentration to the cell with the higher concentration. As concentration increases so does the voltage for all 3 types of cells.
Increasing extracellular K increases the positive charge outside the cell. Therefore an increase in concentration must cause the equilibrium to move to the left hand. To determine the effect of concentration on cell potential using the Nrest equation.
Standard electrode potentials are always specified as the voltage potential under standard conditions 25C 100 mol L-1 as the voltage is dependent upon both temperature and electrolyte concentration. Changing the concentration of one solution in the cell will increase the voltage potential of the cell because you are putting the system further out of equilibrium. The only downside is how the change in tests 2 and 3 are very small and almost negligible.
Hi its me again. The relationship between cell potential and ion concentration is given by the Nernst equation. The electrode potential depends on the equilibrium for example M s M2 aq 2e.
The further the equilibrium is to the right the more negative the electrode potential. As the system discharges the concentration of Reducing Agent ion will increase due. Also using Le Chateliers principle an increase in concentration of Mn2 causes equilibrium to shift as the reaction goes toward the products producing a higher positive voltage.
Im a bit confused about why in 1c if the air pressure is lower and there is a lower concentration of oxygen why the cell potential decreases. The Nernst equation tells us that a half-cell potential will change by 59 millivolts per 10-fold change in the concentration of a substance involved in a one-electron ox. This is the emf of the cell when operating under standard conditions Ie 1 Atmosphere 298K and unit concentration.
Also know how does concentration affect cell potential. I will show how this works by this example. The Effect of Temperature and Concentration on Galvanic Cells.
To optimize the voltage in a GalvanicVoltaic Cell the concentration of the Reducing Agent in the Anodic Side of the system oxidation rxn should be low and the concentration of the Oxidizing Agent ion in the Cathodic side of the system reduction rxn should be high. Of course a requirement is that the the reaction quotient remains at 1 because as soon as it differs the Δ E no longer represents the standard electrical potential of the directly cell and so it must be. As surface area increases so does the voltage for both cells.
How does concentration affect the cell potential. An equal concentration of the solutions will result a cell potential equal to the standard because the logarithm of the reaction quotient will be 0. Any good chemistry text will have a section on this topic.
How does concentration affect the cell potential. How does K affect membrane potential. What affects a galvanic cell.
By the equilibrium law. How does concentration affect cell potential.
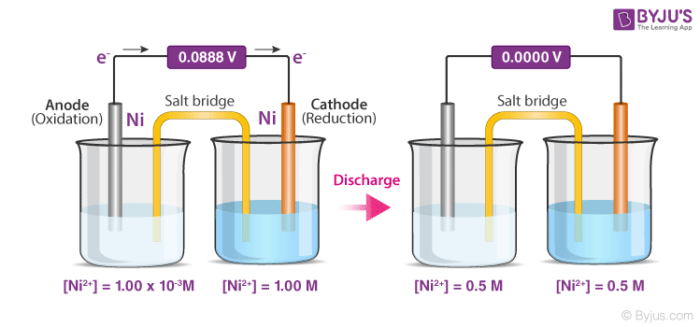
Concentration Cell Definition Details Types And Components With Examples

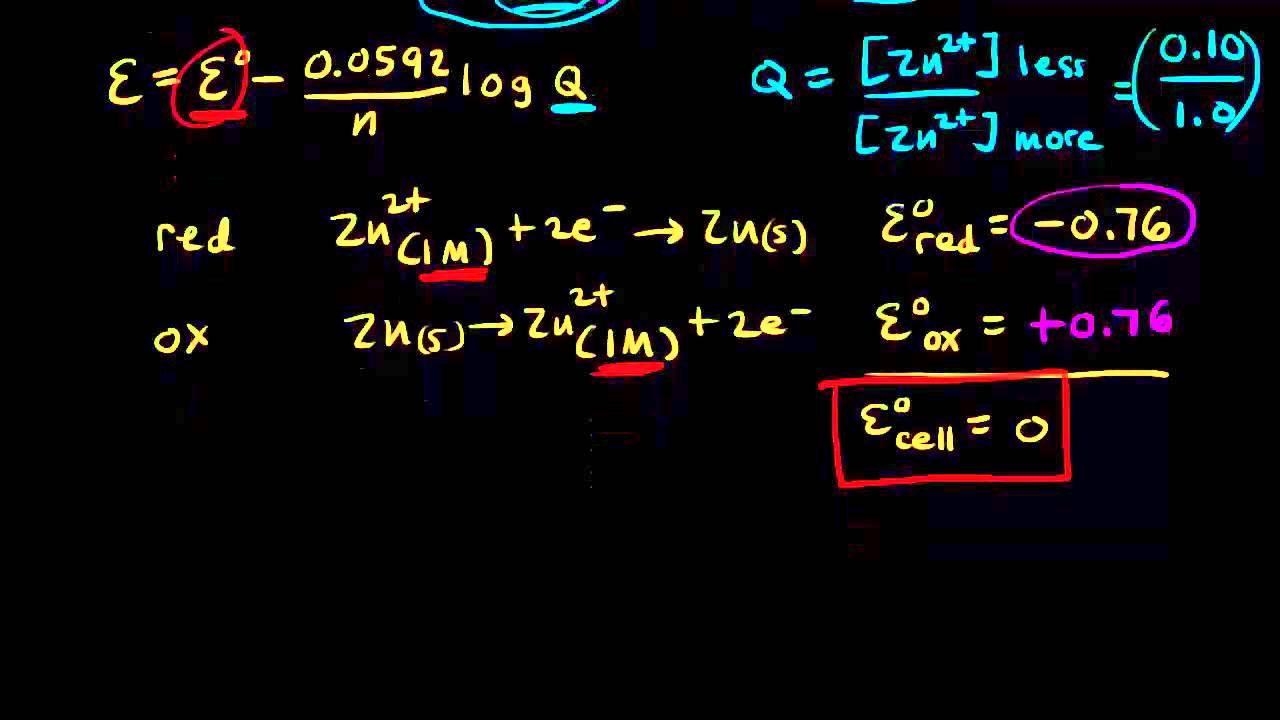
Comments
Post a Comment